What Are the Different Types of Cloud Computing?
- DevOps
- May 24, 2021
The trend of cloud computing is constant in the IT industry. Generally, the term is used by IT businesses, experts, and companies. Nevertheless, the term itself incorporates various types of cloud computing.
Cloud computing is advantageous for companies. It provides flexibility, lowers IT expenses, increases efficiency, enhances data sharing, and scalability.
Moreover, you should know that there are many models and types of cloud computing. Since there is no model perfect for all businesses, you need to recognize the most suitable model by learning about the different cloud computing types.
Selecting the best cloud computing type or model for your company caters to the usability, your company’s size, cost-effectiveness, advantages, requirements, and the variances provided by every kind of cloud computing service.
Hence, you should understand the available models or types and decide the deployment that best meets your company’s requirements.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is all about offering computer resources on-demand through a PAYG (Pay As You Go) model. These resources incorporate databases, virtual devices, data storage, serverless infrastructure, and so forth.
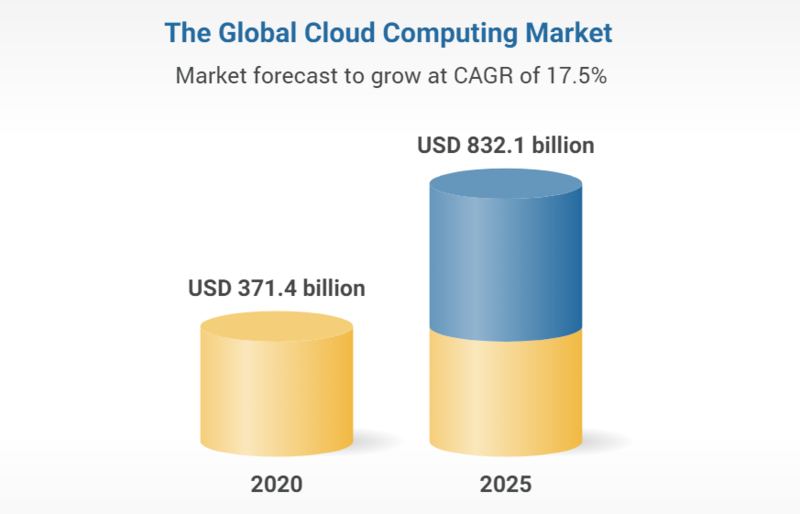
According to report, the cloud computing market size is expected to grow from USD 371.4 billion in 2020 to USD 832.1 billion by 2025 globally.
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing models differ depending on how data communications and sharing occur, how data is stored, and how cloud-based apps run.
Although there are many classifications, 3 main types of cloud computing are found: Private, Public, and Hybrid. We will explore each of them individually, depicting the pros and cons of every type.
1. Private Cloud
According to its name, the private cloud service is intended for single-use. Generally, its resources are found on-premises or a third-party vendor operates it at an offsite area. Third-party providers detach the computer resources through a private, secure network that cannot be shared with other clients. According to report by RightScale, The average business runs 41% of workloads in private cloud.
The private cloud solution is the single tenancy model that is situated within the company’s network and has private exposure only. The company handles it internally on its own and offers all hardware elements. A private cloud is usually a highly expensive model.
Advantages of Private Cloud
- Supports legacy apps.
- Private access makes sure a safe and dedicated solution.
- Extreme level of flexibility enables changes in IT and business requirements without compromising performance and security.
- Government and regulatory compliance are simpler, as the private cloud model features custom-made security.
- High-efficiency levels and SLA (Service Level Agreement) improve functionality.
Disadvantages of Private Cloud
- Needs extremely skilled experts.
- It’s a costly solution.
- Mobile users get restricted access.
- Not relevant for short-term use cases.
- Infrastructure scalability may be limited in case the cloud data center is restricted to on-premise computing resources.
Suitability
- Cloud computing for business helps meet the large data center requirements of large enterprises. Relevant for companies that can invest in high-end technologies.
- Maintains powerful security measures and controls over IT workloads and the fundamental infrastructure.
- Suitable for extremely regulated industries.
2. Public Cloud
Public Cloud is the most common type of cloud computing model, gives the public access to the resources through the web. This can be paid (through a subscription) or free service.
The public cloud’s computing functionality of every provider is not the same. Public cloud solutions provide scalability and elasticity cost-effectively.
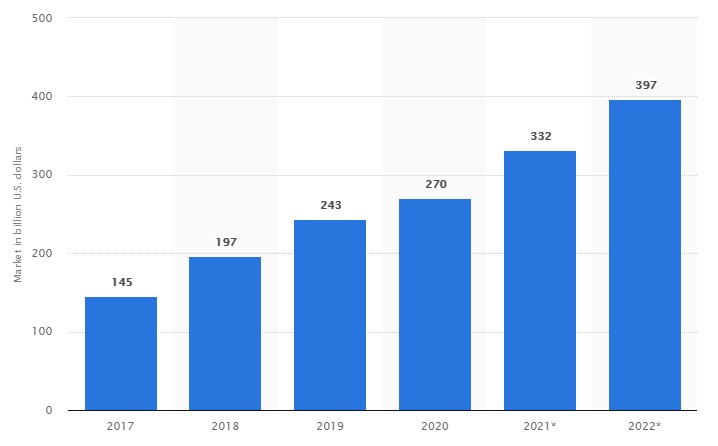
As per Statista, the global public cloud computing market continues to grow and is expected to reach an estimated $397 billion in 2022.
Public Cloud is a multi-tenancy model with complete exposure found anywhere on the web within the boundaries of the service provider. The service provider externally deals with it and fulfills all hardware elements. Usually, a public cloud model’s cost is moderate.
Advantages of Public Cloud
- Anybody can utilize the services online.
- It is highly scalable.
- Agile cost structure enables companies to concentrate on other kinds of investments.
- PAYG pricing model helps you determine the cost level.
- High availability helps you fulfill extra resource needs easily.
- Usage and setup require less technical knowledge.
- Public cloud providers have in-built apps and services preferred for IT and business operations.
- Predictable computing requirements lower possible downtime.
Disadvantages of Public Cloud
- Restricted infrastructure control.
- The ownership cost cannot be predicted and might increase for large-scale users.
- Can’t meet every security need.
- The service provider may limit the use of their software and hardware.
- Can’t totally support the industry standards, legal needs, needs of government policies, etc.
Suitability
- Usable in testing and development ambiances.
- Suitable for companies with predictable computing requirements.
- Relevant in case resource needs vary frequently.
- Suitable if cloud services and apps of public clouds can meet business requirements.
3. Hybrid Cloud
The Hybrid Cloud is a combination of private and public cloud solutions with an integrated infrastructure where the privatization of sensitive apps happens, but common services’ hosting happens in the public cloud. Users can utilize the app and data workloads located in both the public and private clouds.
This is a mix of single and multiple tenancy models with both public and private exposure and is situated inside the service provider’s location and the company’s network.
Both the service provider and the company deal with the hybrid cloud and each of them offers some hardware elements. A hybrid cloud model’s cost is variable, based on which portion is public and which one is private. As per research, 45% of enterprises see hybrid cloud as their top priority and it is the weapon of choice for them.
Advantages of Hybrid Cloud
- The hybrid cloud is extremely authentic as it offers shared services across multiple cloud solutions.
- Government and regulatory compliance, and legacy needs are simpler to fulfill in comparison with a completely public cloud.
- Offers more scalability and flexibility than completely private cloud apps without disturbing security.
- You can utilize both cloud-native and legacy apps.
- Costs are lower than a completely private cloud solution.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Cloud
- Needs high-end tech expertise for establishing, handling, and maintaining the solution.
- Can be costly, particularly compared to the public cloud.
- Infrastructure can be complicated due to the emerging combination of private and public clouds.
- Needs powerful compatibility and integration between the combination of public and private data centers.
Suitability
- Suitable for companies that require optimizing cloud solutions without adjusting a public cloud’s value proposition and a private cloud’s security.
- Usable for companies that need various IT, performance, regulatory, and security needs.
Multi-Cloud Model
Multi-cloud is another type of cloud computing that is similar to the hybrid cloud. It refers to more than a single public cloud provider along with a private cloud.
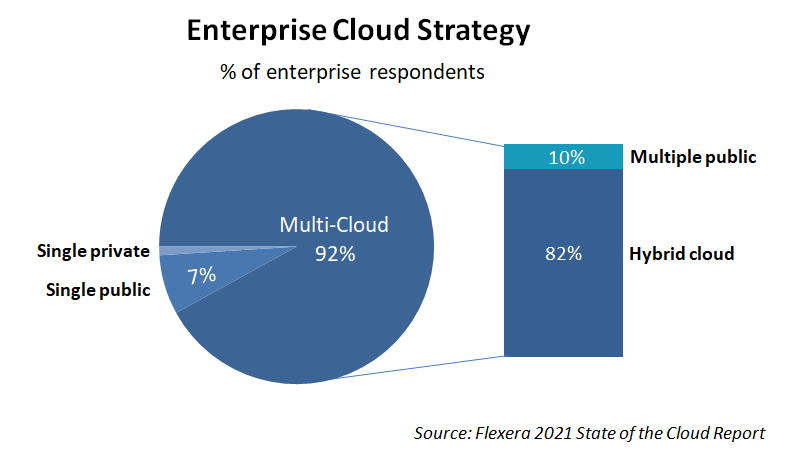
A multi-cloud provides every benefit of a public cloud, but two or more vendors distribute the services you get. Mostly, big companies use a multi-cloud model with complex setups. As per the Flexera report, 92% of the enterprises are following a multi-cloud strategy.
A multi-cloud and a hybrid cloud model might seem to be the same on a superficial level. Nevertheless, these two have some differences also. A hybrid cloud implies the mix of public and private clouds, whereas a multi-cloud model explains how companies utilize a mix of various cloud providers for fulfilling business requirements.
In short, multi-cloud refers to a method, where companies avail apps, resources, microservices, and containers from various cloud providers. A hybrid cloud solution is not a multi-cloud model, but a multi-cloud model may incorporate virtualization.
Benefits of Multi-Cloud Model
In terms of numbers, according to cloud computing statistics, respondents highlight several benefits of multi-cloud environments. Specifically, 46% emphasize its durability, 43% appreciate its adaptability to technological changes, 42% value its flexibility, and 41% recognize its enhanced governance. There are many benefits to multi-cloud model, including:
1. Boost Performance
Cloud service providers with data centers close to a company provide reduced latency, packet loss, and jitter. For enterprises with huge workloads, having multi-cloud providers that are close to them geographically, boosts performance.
Moreover, a multi-cloud approach enables organizations to opt for the solutions that meet their business needs, thereby helping them increase resources and pay for what they utilize only.
2. Abstain from Vendor Lock-In
Companies choose multi-cloud solutions for abstaining from vendor lock-in. Generally, providers make their platforms complex by launching services and functions that stand them out from others. A vendor can’t provide companies with a one-fits-for-all solution.
Hence, businesses need to find the perfect balance between portability and functionality and should opt for a multi-cloud approach.
3. Avoid Shadow IT
Companies can also accidentally choose multi-cloud solutions. In case various business units choose various cloud providers, the company ends up with a bunch of various cloud providers unintentionally. This can yield waste and overlap. The intentional choice of a properly planned multi-cloud method is preferable.
4. Raise Compliance
Generally, companies can’t build and maintain huge amounts of onsite data, needing data storage with other cloud providers.
Many cloud providers don’t have in-built assistance for all importance compliance; hence, companies should use a multi-cloud strategy to make sure compliance with every industry standard.
5. Enhance Resilience
The best cloud providers can also experience an unexpected downtime that can highly impact the capacity of a company to keep services running. Keeping all apps and data with a single provider can be difficult.
Thereby, deploying data and apps using various cloud providers enhances resilience and offers quicker disaster recovery.
When to Use Multi-cloud?
Use a multi-cloud model in case you don’t want to depend on vendors. Moreover, use one in case you find benefits in using various services from various vendors across your company. Go for a multi-cloud solution in case you need better redundancy.
When Not to Use Multi-cloud?
Select another solution in case you don’t wish to invest money and time in a complicated cloud setup. Moreover, choose a different cloud model in case your company does not have multi-cloud vendor IT professionals. And remember that it’s costlier in case you need to use a multi-cloud for replicating your services through redundancy.
Read also: 10 Biggest Cloud Computing Challenges for IT Service Providers
Final Remarks
Cloud computing has changed how organizations worldwide do business in ways that many people don’t understand. Knowing the difference among different types of cloud computing and finding the right fit for a developing business is highly necessitous.
Since cloud computing services will increase constantly, they will offer new scopes to organizations seeking to make innovations and drive business outcomes. While seeking to reap the benefits of these scopes and innovations, you need to select the right cloud provider.













