Cloud Computing in Mobile Apps – Impacts and Challenges
- DevOps
- September 18, 2020
The proliferation of smartphones and internet connectivity has enabled app developers and consumers to store and interact with data in a way that never conceived before.
The availability of unlimited storage and the limitless processing power offered by the cloud has allowed developers to reach new levels of functionality.
Although many companies have made the bumpy transition to cloud computing, some still hesitate to incorporate cloud computing within their mobile app development process.
Native apps indeed remained the norm until now; the recent trends in the app development world have brought mobile cloud computing to the limelight.
Cisco’s research already predicted the rising popularity of mobile cloud apps in 2019. According to their Global Cloud Index, the company predicted that cloud apps would drive 92 percent of the global mobile data traffic by the end of the year.
As the technology further expands, there will be no way for companies to find success without embracing cloud computing for business.
Since most of the mobile cloud computing or MCC conversations are crowded with technical jargon, we begin by touching upon the crucial terms involved in mobile cloud apps. It will not only provide the readers proper understanding of cloud computing but also help them gauge the impact of cloud computing on mobile apps in its true sense.
What is Cloud Computing?
The definition of cloud computing is continuously evolving according to its characteristics, offerings, service, and deployment models. Generally, cloud computing is defined as an on-demand network access to a pool of resources without any interaction with the service provider.
To put it in simple terms, cloud computing ensures quick and easy availability of parts of significant resources to clients who are charged on the basis of usage. The shared resources like mobile apps, software, and other services are provided to smartphone and desktop users on demand.
Moreover, cloud computing allows users to adjust their computing capacity depending on their requirements for a given task at a given time. Users don’t have to worry about the processing power or storage and get the desired results without compromising on the quality.
Read also: Top Cloud Computing Trends
Cloud Mobile App
A mobile cloud app is a mobile application that operates and can be accessed through the cloud. Even though the cloud apps and services have native features, a large part of the processing is carried out on a remote cloud server.
Popular examples of cloud mobile apps include Dropbox, Asana, and Apple’s iCloud services.
Effects of Cloud Computing in Mobile Apps
The introduction of cloud computing in mobile apps has presented an opportunity for developers to add innovative features in apps that no one thought of a few years ago. Below, we outline the impact of cloud computing on the realm of mobile app development.
1. Platform Compatibility
Cloud computing technology reduced the need for developing separate apps for different OS platforms. Unlike native apps, cloud mobile apps are compatible across multiple platforms, which reduce both the development cost and time.
Cloud computing technology allows developers to build a single app and launch it simultaneously across platforms such as Android and iOS. Since the app is stored on the cloud instead of a platform, users do not face any access issues as long as they have a stable internet connection.
2. Cost Reduction
Although the development cost of a native mobile app tends to vary depending on the features, design, and overall complexity of the app. But it is certainly not an inexpensive affair.
Cloud apps; on the other hand, reduces the app development cost since there is only one app that you have to develop for multiple platforms.
The use of a single codebase is an ideal choice for small businesses or startups who don’t have massive budgets to fund a native mobile app for Android and iOS.
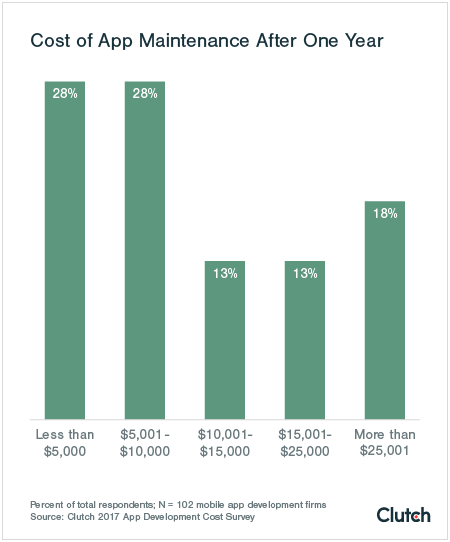
Many novice developers tend to overlook the ongoing maintenance cost associated with an app. For an app to function correctly, it needs to be maintained and updated to eliminate glitches and lags.
According to a survey of 102 mobile app developing firms by Clutch.io, the post-launch maintenance can cost over $25,000 for some apps.
3. Scalability
Scalability refers to the attribute of an application to extend its capacity and functionalities to meet growing users’ demand.
For native and hybrid apps, the scalability of the application comes at a considerable price. In fact, the complexity and cost of scalability may even exceed the initial development cost and complexity for an app that has to scale along the growth of a company.
Fortunately, with cloud apps, the users don’t have to install the new features to their device or update their apps every time you make changes to the app. Of course, this can be done in native apps too, but the cost and complexity involved are a lot higher compared to cloud mobile apps.
Additionally, the users may also encounter poor experience in case the developer doesn’t test the new features thoroughly for bugs. This may lead to users either uninstalling your app, moving to your competitor’s app, or rating it poorly across app stores and social media platforms.
4. No Requirement of Storage Space in the Smartphone
All the data of a cloud-based app is stored on a cloud server that is located remotely and can be accessed through a device with an internet connection. Cloud apps also eliminate the process of installation since they run from a browser.
Hence, cloud apps do not require space on the smartphone for proper operation. Even if there is low storage space on a smartphone, the user does not have to free up space on the phone to access a cloud-based app. They typically work like the web-based apps and can be accessed directly from the central server.
Challenges for Cloud Computing in Mobile Apps
Using the concepts of cloud computing in mobile apps is all about providing a mobile application in the cloud through a cloud service provider and then delivering it to the end-users with an internet connection.
The elements involved in this process have some extent of challenges that hinder the ubiquity of cloud-based apps. Below, we discuss some of the significant challenges posed by cloud mobile apps.
1. Information Security
Security is a primary concern for cloud apps as they store and process users’ data. According to cloud computing statistics, the cloud experiences 45% of all data breaches. App developing firms need to work together with third-party cloud service providers to ensure that all the policies regarding user authentication, access control, and general communications security are followed, and measures are taken to enforce them.
2. Lack of Fast Speed Internet Access
In order to get seamless access to a cloud app, users need to have a stable internet connection. Unfortunately, most parts of the world still suffer from low-speed internet access.
Although most of the providers now offer 4G/LTE services to resolve the connectivity issues, it is still far from becoming mainstream. As such, users are unable to access the rich features of cloud-based apps that require speedy internet access.
3. Resource Deficiency of Mobile Devices
Although mobile devices provide the feature of mobility, it comes at the cost of lesser processing power, memory, and network bandwidth.
The resource deficiency of smartphones is a significant concern for the adoption of cloud-based apps. The disparity between desktops and mobile devices must be lowered in order to run high-end cloud-based applications on smartphones.
Final Words
The use of cloud computing in mobile apps is going to be a significant trend in the coming years. Benefits such as scalability, compatibility, and cost reduction, add a whole lot of substance to the concept of cloud-based mobile apps. However, it is still a technology in the nascent stage.
So, the direction which it might take will become clearer only when companies come forward and address issues like data security, confidentiality, and privacy.













